Sunday, February 21, 2010
February 18, 2010 | NetWitness Discovers Massive ZeuS Compromise
"Kneber Botnet" Targets Corporate Networks and Credentials
HERNDON , VA - February 18, 2010 - NetWitness, the world leader in advanced persistent threat detection and real-time network forensics, announced today that its analysts have discovered a dangerous new ZeuS botnet affecting 75,000 systems in 2,500 organizations around the world. The newly-discovered infestation, dubbed the "Kneber botnet" after the username linking the infected systems worldwide, gathers login credentials to online financial systems, social networking sites and email systems from infested computers and reports the information to miscreants who can use it to break into accounts, steal corporate and government information, and replicate personal, online and financial identities.
NetWitness first discovered the Kneber botnet in January during a routine deployment of the NetWitness advanced monitoring solutions. Deeper investigation revealed an extensive compromise of commercial and government systems that included 68,000 corporate login credentials, access to email systems, online banking sites, Facebook, Yahoo, Hotmail and other social networking credentials, 2,000 SSL certificate files, and dossier-level data sets on individuals including complete dumps of entire identities from victim machines.
Discussing the importance of the Kneber botnet, Amit Yoran, CEO of NetWitness and former Director of the National Cyber Security Division, said, "While Operation Aurora shed light on advanced threats from sponsored adversaries, the number of compromised companies and organizations pales in comparison to this single botnet. These large-scale compromises of enterprise networks have reached epidemic levels. Cyber criminal elements, like the Kneber crew quietly and diligently target and compromise thousands of government and commercial organizations across the globe. Conventional malware protection and signature based intrusion detection systems are by definition inadequate for addressing Kneber or most other advanced threats. Organizations which focus on compliance as the objective of their information security programs and have not kept pace with the rapid advances of the threat environment will not see this Trojan until the damage already has occurred. Systems compromised by this botnet provide the attackers not only user credentials and confidential information, but remote access inside the compromised networks."
"Many security analysts tend to classify ZeuS solely as a Trojan that steals banking information," stated Alex Cox, the Principal Analyst at NetWitness responsible for uncovering the Kneber-bot, "but that viewpoint is naive. When we began to detect the correlation among both the methodology used by the Kneber crew to attack victim machines and the wide variety of data sets harvested, it became clear that security teams must rethink their entire perspective on advanced threats such as ZeuS and consider more diverse mission objectives."
Over half the machines infected with Kneber also were infected with Waledac, a peer to peer botnet. The coexistence of ZeuS and Waledac suggests the goals of resilience and survivability and potential deeper cross-crew collaboration in the criminal underground.
"NetWitness enables the discovery of malicious code like Kneber - before things get critical and valuable data is lost," said Cox. "It is 100% certain that many organizations have no idea they are victimized by these types of problems because they're just not tooled to see them on their networks. The Kneber botnet is just one category of advanced threat that organizations have been facing the past few years that they are still largely ignorant or blind to today."
To download a copy of the NetWitness Kneber whitepaper, visit http://www.netwitness.com.
About NetWitness
NetWitness® Corporation is the world leader in real-time network forensics and automated threat intelligence solutions, helping government and commercial organizations detect, prioritize and remediate complex IT risks. NetWitness solutions concurrently solve a wide variety of information security problems including: advanced persistent threat management; sensitive data discovery and advanced data leakage detection; malware activity discovery; insider threat management; policy and controls verification and e-discovery. Originally developed for the US Intelligence Community, NetWitness has evolved to provide enterprises around the world with breakthrough methods of network content analysis and host-based risk discovery and prioritization. NetWitness customers include Defense, National Law Enforcement and Intelligence Agencies, Top US and European Banks, Critical Infrastructure, and Global 1000 organizations. NetWitness has offices in the U.S. and the U.K. and partners throughout North and South America, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
To download the freeware version of NetWitness Investigator, visit http://download.netwitness.com . For more information about securing your entire organization with NetWitness NextGen, contact: sales@netwitness.com . Twitter handle: NetWitness .
Media Contact:
Steve Ward | (703) 994-9349 | pr@netwitness.com
Botnet revelation shows darker underbelly of malware
http://www.cio.com.au/article/336814/botnet_revelation_shows_darker_underbelly_malware?fp=39&fpid=25592
NetWitness first discovered the Kneber botnet in January during a routine deployment of the NetWitness advanced monitoring solutions. Deeper investigation revealed an extensive compromise of commercial and government systems that included 68,000 corporate login credentials, access to email systems, online banking sites, Facebook, Yahoo, Hotmail and other social networking credentials, 2,000 SSL certificate files, and dossier-level data sets on individuals including complete dumps of entire identities from victim machines.
Discussing the importance of the Kneber botnet, Amit Yoran, CEO of NetWitness and former Director of the National Cyber Security Division, said, "While Operation Aurora shed light on advanced threats from sponsored adversaries, the number of compromised companies and organizations pales in comparison to this single botnet. These large-scale compromises of enterprise networks have reached epidemic levels. Cyber criminal elements, like the Kneber crew quietly and diligently target and compromise thousands of government and commercial organizations across the globe. Conventional malware protection and signature based intrusion detection systems are by definition inadequate for addressing Kneber or most other advanced threats. Organizations which focus on compliance as the objective of their information security programs and have not kept pace with the rapid advances of the threat environment will not see this Trojan until the damage already has occurred. Systems compromised by this botnet provide the attackers not only user credentials and confidential information, but remote access inside the compromised networks."
"Many security analysts tend to classify ZeuS solely as a Trojan that steals banking information," stated Alex Cox, the Principal Analyst at NetWitness responsible for uncovering the Kneber-bot, "but that viewpoint is naive. When we began to detect the correlation among both the methodology used by the Kneber crew to attack victim machines and the wide variety of data sets harvested, it became clear that security teams must rethink their entire perspective on advanced threats such as ZeuS and consider more diverse mission objectives."
Over half the machines infected with Kneber also were infected with Waledac, a peer to peer botnet. The coexistence of ZeuS and Waledac suggests the goals of resilience and survivability and potential deeper cross-crew collaboration in the criminal underground.
"NetWitness enables the discovery of malicious code like Kneber - before things get critical and valuable data is lost," said Cox. "It is 100% certain that many organizations have no idea they are victimized by these types of problems because they're just not tooled to see them on their networks. The Kneber botnet is just one category of advanced threat that organizations have been facing the past few years that they are still largely ignorant or blind to today."
To download a copy of the NetWitness Kneber whitepaper, visit http://www.netwitness.com.
About NetWitness
NetWitness® Corporation is the world leader in real-time network forensics and automated threat intelligence solutions, helping government and commercial organizations detect, prioritize and remediate complex IT risks. NetWitness solutions concurrently solve a wide variety of information security problems including: advanced persistent threat management; sensitive data discovery and advanced data leakage detection; malware activity discovery; insider threat management; policy and controls verification and e-discovery. Originally developed for the US Intelligence Community, NetWitness has evolved to provide enterprises around the world with breakthrough methods of network content analysis and host-based risk discovery and prioritization. NetWitness customers include Defense, National Law Enforcement and Intelligence Agencies, Top US and European Banks, Critical Infrastructure, and Global 1000 organizations. NetWitness has offices in the U.S. and the U.K. and partners throughout North and South America, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
To download the freeware version of NetWitness Investigator, visit http://download.netwitness.com . For more information about securing your entire organization with NetWitness NextGen, contact: sales@netwitness.com . Twitter handle: NetWitness .
Media Contact:
Steve Ward | (703) 994-9349 | pr@netwitness.com
Botnet revelation shows darker underbelly of malware
http://www.cio.com.au/article/336814/botnet_revelation_shows_darker_underbelly_malware?fp=39&fpid=25592
Kneber was built using a well-established toolkit for aggregating botnets called ZeuS that has been around for years
Information gathered about a newly discovered botnet called Kneber indicates that multiple infections by different malware on the same host could work together as a sophisticated mechanism to give all the malware a better survival rate.
The sheer size of the Kneber botnet -- 74,000 compromised computers in 2,400 different companies -- attracted most of the attention when Kneber was revealed Thursday. But how it interacts with other malware networks suggests a symbiotic relationship that ultimately makes each botnet more resistant to being dismantled, says Alex Cox, the senior consultant in the research department at NetWitness who discovered Kneber.
Kneber was built using a well-established toolkit for aggregating botnets called ZeuS that has been around for years. Kneber is an example of just one botnet built with the toolkit, but because Cox captured 75GB of log data from the command-and-control server, he was able to examine detailed characteristics of the computers ZeuS took over.
What he found is that more than half the 74,000 compromised computers -- bots -- within Kneber were also found infected with other malware that uses a different command-and-control structure. If one of the criminal networks were disabled, the other could be used to build it up again,
"At the very least, two separate botnet families with different [command-and-control] infrastructures can provide fault tolerance and recoverability in the event that one [command-and-control] mechanism is taken down by security efforts," he says in his written analysis of the Kneber botnet.
In this case, more than half the machines that made up the botnet were infected with both ZeuS, which steals user data, and Waledac, a spamming malware that uses peer-to-peer mechanisms to spread more infections, he says. He can't conclude for sure that they're working together in this case, but the presence of both introduces an interesting possibility: If the ZeuS command-and-control infrastructure is cut down, the owner of the ZeuS botnet could go to the person running the Waledac botnet and pay for it to push a ZeuS upgrade that brings the ZeuS bots back online reporting to a new server, he says.
Alternatively, a single group could run both the ZeuS and Waledac botnets and push the upgrade itself. "From a disaster-recovery perspective, it makes sense," Cox says.
"I am also a victim of cyber-stalkerby the Associate Vice President of the C ..."
Michelle"It's worth remembering that any future
Ady Berry"They have 4 servers:
ASHS Student"Thanks for the article. In general I agree and I like using clouds and doin ..."
Tom Peruzzi"Perhaps they should look at the quality of the service rather than protecti ..."
Glenn Irvine
The Kneber server log contained individuals' passwords to sites including Facebook and Yahoo as well as a slew of financial sites including CitiBank, Wells Fargo, PayPal, Citizens Bank and HSBC Bank, according to Cox's report on Kneber.
Cox discovered Kneber Jan. 26 while working at a NetWitness customer site. He found a machine infected with ZeuS that was downloading other malware executables. He traced the traffic back to a ZeuS command-and-control server in Germany, where he was able to grab a month's worth of the server's log data. He won't say he accomplished these actions.
The botnet got its name from hilarykneber@yahoo.com, the registrant listed for the original domain used to pull together various components of the botnet. That same registrant has been associated with seeking other malware including PDF and Flash exploits as well as Trojan installs.
The same registrant is also listed on multiple Web sites seeking money mules -- people who accept illegal transfers of money into their bank accounts and forward them to other bank accounts in an effort to make the funds unrecoverable by the actual owners.
Kneber has been active since March 25, 2009, and most of the sites associated with its activities are in China, according to their underlying IP addresses, NetWitness says. About 17% of these sites are in the United States.
Cox also links Kneber to a phishing attack against U.S. government agencies that sends e-mails apparently from the National Security Agency that urges recipients to click on links that download the malware.
He gives significance to the fact that one of the things Kneber harvests is social networking usernames and passwords. These can be used to get into social networking accounts where they can post links to infected sites. Social network friends are more likely to trust these links because they seem to be posted by people they trust.
Social network accounts can also be mined for personal data that can be useful in further compromising individuals' financial accounts. For example, if social networking accounts yield mothers' maiden names, they might be used to reset passwords of bank accounts, giving attackers a way to get in and transfer money out.
Thursday, February 4, 2010
How To Become A Hacker
Eric Steven Raymond
Copyright © 2001 Eric S. Raymond
Table of Contents
Why This Document?
If you are reading a snapshot of this document offline, the current version lives at http://catb.org/~esr/faqs/hacker-howto.html.
Note: there is a list of Frequently Asked Questions at the end of this document. Please read these—twice—before mailing me any questions about this document.
Numerous translations of this document are available: Arabic Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (Simplified), Danish, Dutch, Estonian, Farsi, Finnish, German, Greek Hebrew, Italian Japanese, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazilian), Romanian Russian Spanish, Turkish, and Swedish. Note that since this document changes occasionally, they may be out of date to varying degrees.
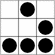
The five-dots-in-nine-squares diagram that decorates this document is called a glider. It is a simple pattern with some surprising properties in a mathematical simulation called Life that has fascinated hackers for many years. I think it makes a good visual emblem for what hackers are like — abstract, at first a bit mysterious-seeming, but a gateway to a whole world with an intricate logic of its own. Read more about the glider emblem here.
What Is a Hacker?
There is a community, a shared culture, of expert programmers and networking wizards that traces its history back through decades to the first time-sharing minicomputers and the earliest ARPAnet experiments. The members of this culture originated the term ‘hacker’. Hackers built the Internet. Hackers made the Unix operating system what it is today. Hackers run Usenet. Hackers make the World Wide Web work. If you are part of this culture, if you have contributed to it and other people in it know who you are and call you a hacker, you're a hacker.
The hacker mind-set is not confined to this software-hacker culture. There are people who apply the hacker attitude to other things, like electronics or music — actually, you can find it at the highest levels of any science or art. Software hackers recognize these kindred spirits elsewhere and may call them ‘hackers’ too — and some claim that the hacker nature is really independent of the particular medium the hacker works in. But in the rest of this document we will focus on the skills and attitudes of software hackers, and the traditions of the shared culture that originated the term ‘hacker’.
There is another group of people who loudly call themselves hackers, but aren't. These are people (mainly adolescent males) who get a kick out of breaking into computers and phreaking the phone system. Real hackers call these people ‘crackers’ and want nothing to do with them. Real hackers mostly think crackers are lazy, irresponsible, and not very bright, and object that being able to break security doesn't make you a hacker any more than being able to hotwire cars makes you an automotive engineer. Unfortunately, many journalists and writers have been fooled into using the word ‘hacker’ to describe crackers; this irritates real hackers no end.
The basic difference is this: hackers build things, crackers break them.
If you want to be a hacker, keep reading. If you want to be a cracker, go read the alt.2600 newsgroup and get ready to do five to ten in the slammer after finding out you aren't as smart as you think you are. And that's all I'm going to say about crackers.

The Hacker Attitude
But if you think of cultivating hacker attitudes as just a way to gain acceptance in the culture, you'll miss the point. Becoming the kind of person who believes these things is important for you — for helping you learn and keeping you motivated. As with all creative arts, the most effective way to become a master is to imitate the mind-set of masters — not just intellectually but emotionally as well.
Or, as the following modern Zen poem has it:
To follow the path:
look to the master,
follow the master,
walk with the master,
see through the master,
become the master.
1. The world is full of fascinating problems waiting to be solved.
If you aren't the kind of person that feels this way naturally, you'll need to become one in order to make it as a hacker. Otherwise you'll find your hacking energy is sapped by distractions like sex, money, and social approval.
(You also have to develop a kind of faith in your own learning capacity — a belief that even though you may not know all of what you need to solve a problem, if you tackle just a piece of it and learn from that, you'll learn enough to solve the next piece — and so on, until you're done.)
2. No problem should ever have to be solved twice.
To behave like a hacker, you have to believe that the thinking time of other hackers is precious — so much so that it's almost a moral duty for you to share information, solve problems and then give the solutions away just so other hackers can solve new problems instead of having to perpetually re-address old ones.
Note, however, that "No problem should ever have to be solved twice." does not imply that you have to consider all existing solutions sacred, or that there is only one right solution to any given problem. Often, we learn a lot about the problem that we didn't know before by studying the first cut at a solution. It's OK, and often necessary, to decide that we can do better. What's not OK is artificial technical, legal, or institutional barriers (like closed-source code) that prevent a good solution from being re-used and force people to re-invent wheels.
(You don't have to believe that you're obligated to give all your creative product away, though the hackers that do are the ones that get most respect from other hackers. It's consistent with hacker values to sell enough of it to keep you in food and rent and computers. It's fine to use your hacking skills to support a family or even get rich, as long as you don't forget your loyalty to your art and your fellow hackers while doing it.)
3. Boredom and drudgery are evil.
To behave like a hacker, you have to believe this enough to want to automate away the boring bits as much as possible, not just for yourself but for everybody else (especially other hackers).
(There is one apparent exception to this. Hackers will sometimes do things that may seem repetitive or boring to an observer as a mind-clearing exercise, or in order to acquire a skill or have some particular kind of experience you can't have otherwise. But this is by choice — nobody who can think should ever be forced into a situation that bores them.)
4. Freedom is good.
(This isn't the same as fighting all authority. Children need to be guided and criminals restrained. A hacker may agree to accept some kinds of authority in order to get something he wants more than the time he spends following orders. But that's a limited, conscious bargain; the kind of personal surrender authoritarians want is not on offer.)
Authoritarians thrive on censorship and secrecy. And they distrust voluntary cooperation and information-sharing — they only like ‘cooperation’ that they control. So to behave like a hacker, you have to develop an instinctive hostility to censorship, secrecy, and the use of force or deception to compel responsible adults. And you have to be willing to act on that belief.
5. Attitude is no substitute for competence.
Therefore, you have to learn to distrust attitude and respect competence of every kind. Hackers won't let posers waste their time, but they worship competence — especially competence at hacking, but competence at anything is valued. Competence at demanding skills that few can master is especially good, and competence at demanding skills that involve mental acuteness, craft, and concentration is best.
If you revere competence, you'll enjoy developing it in yourself — the hard work and dedication will become a kind of intense play rather than drudgery. That attitude is vital to becoming a hacker.

Basic Hacking Skills
This toolkit changes slowly over time as technology creates new skills and makes old ones obsolete. For example, it used to include programming in machine language, and didn't until recently involve HTML. But right now it pretty clearly includes the following:
1. Learn how to program.
I used to recommend Java as a good language to learn early, but this critique has changed my mind (search for “The Pitfalls of Java as a First Programming Language” within it). A hacker cannot, as they devastatingly put it “approach problem-solving like a plumber in a hardware store”; you have to know what the components actually do. Now I think it is probably best to learn C and Lisp first, then Java.
There is perhaps a more general point here. If a language does too much for you, it may be simultaneously a good tool for production and a bad one for learning. It's not only languages that have this problem; web application frameworks like RubyOnRails, CakePHP, Django may make it too easy to reach a superficial sort of understanding that will leave you without resources when you have to tackle a hard problem, or even just debug the solution to an easy one.
If you get into serious programming, you will have to learn C, the core language of Unix. C++ is very closely related to C; if you know one, learning the other will not be difficult. Neither language is a good one to try learning as your first, however. And, actually, the more you can avoid programming in C the more productive you will be.
C is very efficient, and very sparing of your machine's resources. Unfortunately, C gets that efficiency by requiring you to do a lot of low-level management of resources (like memory) by hand. All that low-level code is complex and bug-prone, and will soak up huge amounts of your time on debugging. With today's machines as powerful as they are, this is usually a bad tradeoff — it's smarter to use a language that uses the machine's time less efficiently, but your time much more efficiently. Thus, Python.
Other languages of particular importance to hackers include Perl and LISP. Perl is worth learning for practical reasons; it's very widely used for active web pages and system administration, so that even if you never write Perl you should learn to read it. Many people use Perl in the way I suggest you should use Python, to avoid C programming on jobs that don't require C's machine efficiency. You will need to be able to understand their code.
LISP is worth learning for a different reason — the profound enlightenment experience you will have when you finally get it. That experience will make you a better programmer for the rest of your days, even if you never actually use LISP itself a lot. (You can get some beginning experience with LISP fairly easily by writing and modifying editing modes for the Emacs text editor, or Script-Fu plugins for the GIMP.)
It's best, actually, to learn all five of Python, C/C++, Java, Perl, and LISP. Besides being the most important hacking languages, they represent very different approaches to programming, and each will educate you in valuable ways.
But be aware that you won't reach the skill level of a hacker or even merely a programmer simply by accumulating languages — you need to learn how to think about programming problems in a general way, independent of any one language. To be a real hacker, you need to get to the point where you can learn a new language in days by relating what's in the manual to what you already know. This means you should learn several very different languages.
I can't give complete instructions on how to learn to program here — it's a complex skill. But I can tell you that books and courses won't do it — many, maybe most of the best hackers are self-taught. You can learn language features — bits of knowledge — from books, but the mind-set that makes that knowledge into living skill can be learned only by practice and apprenticeship. What will do it is (a) reading code and (b) writing code.
Peter Norvig, who is one of Google's top hackers and the co-author of the most widely used textbook on AI, has written an excellent essay called Teach Yourself Programming in Ten Years. His "recipe for programming success" is worth careful attention.
Learning to program is like learning to write good natural language. The best way to do it is to read some stuff written by masters of the form, write some things yourself, read a lot more, write a little more, read a lot more, write some more ... and repeat until your writing begins to develop the kind of strength and economy you see in your models.
Finding good code to read used to be hard, because there were few large programs available in source for fledgeling hackers to read and tinker with. This has changed dramatically; open-source software, programming tools, and operating systems (all built by hackers) are now widely available. Which brings me neatly to our next topic...
2. Get one of the open-source Unixes and learn to use and run it.
Yes, there are other operating systems in the world besides Unix. But they're distributed in binary — you can't read the code, and you can't modify it. Trying to learn to hack on a Microsoft Windows machine or under any other closed-source system is like trying to learn to dance while wearing a body cast.
Under Mac OS X it's possible, but only part of the system is open source — you're likely to hit a lot of walls, and you have to be careful not to develop the bad habit of depending on Apple's proprietary code. If you concentrate on the Unix under the hood you can learn some useful things.
Unix is the operating system of the Internet. While you can learn to use the Internet without knowing Unix, you can't be an Internet hacker without understanding Unix. For this reason, the hacker culture today is pretty strongly Unix-centered. (This wasn't always true, and some old-time hackers still aren't happy about it, but the symbiosis between Unix and the Internet has become strong enough that even Microsoft's muscle doesn't seem able to seriously dent it.)
So, bring up a Unix — I like Linux myself but there are other ways (and yes, you can run both Linux and Microsoft Windows on the same machine). Learn it. Run it. Tinker with it. Talk to the Internet with it. Read the code. Modify the code. You'll get better programming tools (including C, LISP, Python, and Perl) than any Microsoft operating system can dream of hosting, you'll have fun, and you'll soak up more knowledge than you realize you're learning until you look back on it as a master hacker.
For more about learning Unix, see The Loginataka. You might also want to have a look at The Art Of Unix Programming.
To get your hands on a Linux, see the Linux Online! site; you can download from there or (better idea) find a local Linux user group to help you with installation.
During the first ten years of this HOWTO's life, I reported that from a new user's point of view, all Linux distributions are almost equivalent. But in 2006-2007, an actual best choice emerged: Ubuntu. While other distros have their own areas of strength, Ubuntu is far and away the most accessible to Linux newbies.
You can find BSD Unix help and resources at www.bsd.org.
A good way to dip your toes in the water is to boot up what Linux fans call a live CD, a distribution that runs entirely off a CD without having to modify your hard disk. This will be slow, because CDs are slow, but it's a way to get a look at the possibilities without having to do anything drastic.
I have written a primer on the basics of Unix and the Internet.
I used to recommend against installing either Linux or BSD as a solo project if you're a newbie. Nowadays the installers have gotten good enough that doing it entirely on your own is possible, even for a newbie. Nevertheless, I still recommend making contact with your local Linux user's group and asking for help. It can't hurt, and may smooth the process.
3. Learn how to use the World Wide Web and write HTML.
This doesn't just mean learning how to drive a browser (anyone can do that), but learning how to write HTML, the Web's markup language. If you don't know how to program, writing HTML will teach you some mental habits that will help you learn. So build a home page. Try to stick to XHTML, which is a cleaner language than classic HTML. (There are good beginner tutorials on the Web; here's one.)
But just having a home page isn't anywhere near good enough to make you a hacker. The Web is full of home pages. Most of them are pointless, zero-content sludge — very snazzy-looking sludge, mind you, but sludge all the same (for more on this see The HTML Hell Page).
To be worthwhile, your page must have content — it must be interesting and/or useful to other hackers. And that brings us to the next topic...
4. If you don't have functional English, learn it.
Back around 1991 I learned that many hackers who have English as a second language use it in technical discussions even when they share a birth tongue; it was reported to me at the time that English has a richer technical vocabulary than any other language and is therefore simply a better tool for the job. For similar reasons, translations of technical books written in English are often unsatisfactory (when they get done at all).
Linus Torvalds, a Finn, comments his code in English (it apparently never occurred to him to do otherwise). His fluency in English has been an important factor in his ability to recruit a worldwide community of developers for Linux. It's an example worth following.
Being a native English-speaker does not guarantee that you have language skills good enough to function as a hacker. If your writing is semi-literate, ungrammatical, and riddled with misspellings, many hackers (including myself) will tend to ignore you. While sloppy writing does not invariably mean sloppy thinking, we've generally found the correlation to be strong — and we have no use for sloppy thinkers. If you can't yet write competently, learn to.

Status in the Hacker Culture
Accordingly, when you play the hacker game, you learn to keep score primarily by what other hackers think of your skill (this is why you aren't really a hacker until other hackers consistently call you one). This fact is obscured by the image of hacking as solitary work; also by a hacker-cultural taboo (gradually decaying since the late 1990s but still potent) against admitting that ego or external validation are involved in one's motivation at all.
Specifically, hackerdom is what anthropologists call a gift culture. You gain status and reputation in it not by dominating other people, nor by being beautiful, nor by having things other people want, but rather by giving things away. Specifically, by giving away your time, your creativity, and the results of your skill.
There are basically five kinds of things you can do to be respected by hackers:
1. Write open-source software
(We used to call these works “free software”, but this confused too many people who weren't sure exactly what “free” was supposed to mean. Most of us now prefer the term “open-source” software).
Hackerdom's most revered demigods are people who have written large, capable programs that met a widespread need and given them away, so that now everyone uses them.
But there's a bit of a fine historical point here. While hackers have always looked up to the open-source developers among them as our community's hardest core, before the mid-1990s most hackers most of the time worked on closed source. This was still true when I wrote the first version of this HOWTO in 1996; it took the mainstreaming of open-source software after 1997 to change things. Today, "the hacker community" and "open-source developers" are two descriptions for what is essentially the same culture and population — but it is worth remembering that this was not always so. (For more on this, see the section called “Historical Note: Hacking, Open Source, and Free Software”.)
2. Help test and debug open-source software
If you're a newbie, try to find a program under development that you're interested in and be a good beta-tester. There's a natural progression from helping test programs to helping debug them to helping modify them. You'll learn a lot this way, and generate good karma with people who will help you later on.
3. Publish useful information
Maintainers of major technical FAQs get almost as much respect as open-source authors.
4. Help keep the infrastructure working
People who do this sort of thing well get a lot of respect, because everybody knows these jobs are huge time sinks and not as much fun as playing with code. Doing them shows dedication.
5. Serve the hacker culture itself
The hacker culture doesn't have leaders, exactly, but it does have culture heroes and tribal elders and historians and spokespeople. When you've been in the trenches long enough, you may grow into one of these. Beware: hackers distrust blatant ego in their tribal elders, so visibly reaching for this kind of fame is dangerous. Rather than striving for it, you have to sort of position yourself so it drops in your lap, and then be modest and gracious about your status.

The Hacker/Nerd Connection
For this reason, many hackers have adopted the label ‘geek’ as a badge of pride — it's a way of declaring their independence from normal social expectations (as well as a fondness for other things like science fiction and strategy games that often go with being a hacker). The term 'nerd' used to be used this way back in the 1990s, back when 'nerd' was a mild pejorative and 'geek' a rather harsher one; sometime after 2000 they switched places, at least in U.S. popular culture, and there is now even a significant geek-pride culture among people who aren't techies.
If you can manage to concentrate enough on hacking to be good at it and still have a life, that's fine. This is a lot easier today than it was when I was a newbie in the 1970s; mainstream culture is much friendlier to techno-nerds now. There are even growing numbers of people who realize that hackers are often high-quality lover and spouse material.
If you're attracted to hacking because you don't have a life, that's OK too — at least you won't have trouble concentrating. Maybe you'll get a life later on.

Points For Style
- Learn to write your native language well. Though it's a common stereotype that programmers can't write, a surprising number of hackers (including all the most accomplished ones I know of) are very able writers.
- Read science fiction. Go to science fiction conventions (a good way to meet hackers and proto-hackers).
- Train in a martial-arts form. The kind of mental discipline required for martial arts seems to be similar in important ways to what hackers do. The most popular forms among hackers are definitely Asian empty-hand arts such as Tae Kwon Do, various forms of Karate, Kung Fu, Aikido, or Ju Jitsu. Western fencing and Asian sword arts also have visible followings. In places where it's legal, pistol shooting has been rising in popularity since the late 1990s. The most hackerly martial arts are those which emphasize mental discipline, relaxed awareness, and control, rather than raw strength, athleticism, or physical toughness.
- Study an actual meditation discipline. The perennial favorite among hackers is Zen (importantly, it is possible to benefit from Zen without acquiring a religion or discarding one you already have). Other styles may work as well, but be careful to choose one that doesn't require you to believe crazy things.
- Develop an analytical ear for music. Learn to appreciate peculiar kinds of music. Learn to play some musical instrument well, or how to sing.
- Develop your appreciation of puns and wordplay.
Work as intensely as you play and play as intensely as you work. For true hackers, the boundaries between "play", "work", "science" and "art" all tend to disappear, or to merge into a high-level creative playfulness. Also, don't be content with a narrow range of skills. Though most hackers self-describe as programmers, they are very likely to be more than competent in several related skills — system administration, web design, and PC hardware troubleshooting are common ones. A hacker who's a system administrator, on the other hand, is likely to be quite skilled at script programming and web design. Hackers don't do things by halves; if they invest in a skill at all, they tend to get very good at it.
Finally, a few things not to do.
- Don't use a silly, grandiose user ID or screen name.
- Don't get in flame wars on Usenet (or anywhere else).
- Don't call yourself a ‘cyberpunk’, and don't waste your time on anybody who does.
- Don't post or email writing that's full of spelling errors and bad grammar.
The problem with screen names or handles deserves some amplification. Concealing your identity behind a handle is a juvenile and silly behavior characteristic of crackers, warez d00dz, and other lower life forms. Hackers don't do this; they're proud of what they do and want it associated with their real names. So if you have a handle, drop it. In the hacker culture it will only mark you as a loser.

Historical Note: Hacking, Open Source, and Free Software
The hacker ethos and community as I have described it here long predates the emergence of Linux after 1990; I first became involved with it around 1976, and, its roots are readily traceable back to the early 1960s. But before Linux, most hacking was done on either proprietary operating systems or a handful of quasi-experimental homegrown systems like MIT's ITS that were never deployed outside of their original academic niches. While there had been some earlier (pre-Linux) attempts to change this situation, their impact was at best very marginal and confined to communities of dedicated true believers which were tiny minorities even within the hacker community, let alone with respect to the larger world of software in general.
What is now called "open source" goes back as far as the hacker community does, but until 1985 it was an unnamed folk practice rather than a conscious movement with theories and manifestos attached to it. This prehistory ended when, in 1985, arch-hacker Richard Stallman ("RMS") tried to give it a name — "free software". But his act of naming was also an act of claiming; he attached ideological baggage to the "free software" label which much of the existing hacker community never accepted. As a result, the "free software" label was loudly rejected by a substantial minority of the hacker community (especially among those associated with BSD Unix), and used with serious but silent reservations by a majority of the remainder (including myself).
Despite these reservations, RMS's claim to define and lead the hacker community under the "free software" banner broadly held until the miid-1990s. It was seriously challenged only by the rise of Linux. Linux gave open-source development a natural home. Many projects issued under terms we would now call open-source migrated from proprietary Unixes to Linux. The community around Linux grew explosively, becoming far larger and more heterogenous than the pre-Linux hacker culture. RMS determinedly attempted to co-opt all this activity into his "free software" movement, but was thwarted by both the exploding diversity of the Linux community and the public skepticism of its founder, Linus Torvalds. Torvalds continued to use the term "free software" for lack of any alternative, but publicly rejected RMS's ideological baggage. Many younger hackers followed suit.
In 1996, when I first published this Hacker HOWTO, the hacker community was rapidly reorganizing around Linux and a handful of other open-source operating systems (notably those descended from BSD Unix). Community memory of the fact that most of us had spent decades developing closed-source software on closed-source operating systems had not yet begun to fade, but that fact was already beginning to seem like part of a dead past; hackers were, increasingly, defining themselves as hackers by their attachments to open-source projects such as Linux or Apache.
The term "open source", however, had not yet emerged; it would not do so until early 1998. When it did, most of hacker community adopted it within the following six months; the exceptions were a minority ideologically attached to the term "free software". Since 1998, and especially after about 2003, the identification of 'hacking' with 'open-source (and free software) development' has become extremely close. Today there is little point in attempting to distinguish between these categories, and it seems unlikely that will change in the future.
It is worth remembering, however, that this was not always so.

Other Resources
There is a document called How To Be A Programmer that is an excellent complement to this one. It has valuable advice not just about coding and skillsets, but about how to function on a programming team.
I have also written A Brief History Of Hackerdom.
I have written a paper, The Cathedral and the Bazaar, which explains a lot about how the Linux and open-source cultures work. I have addressed this topic even more directly in its sequel Homesteading the Noosphere.
Rick Moen has written an excellent document on how to run a Linux user group.
Rick Moen and I have collaborated on another document on How To Ask Smart Questions. This will help you seek assistance in a way that makes it more likely that you will actually get it.
If you need instruction in the basics of how personal computers, Unix, and the Internet work, see The Unix and Internet Fundamentals HOWTO.
When you release software or write patches for software, try to follow the guidelines in the Software Release Practice HOWTO.
If you enjoyed the Zen poem, you might also like Rootless Root: The Unix Koans of Master Foo.

Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: How do I tell if I am already a hacker?
- Q: Will you teach me how to hack?
- Q: How can I get started, then?
- Q: When do you have to start? Is it too late for me to learn?
- Q: How long will it take me to learn to hack?
- Q: Is Visual Basic a good language to start with?
- Q: Would you help me to crack a system, or teach me how to crack?
- Q: How can I get the password for someone else's account?
- Q: How can I break into/read/monitor someone else's email?
- Q: How can I steal channel op privileges on IRC?
- Q: I've been cracked. Will you help me fend off further attacks?
- Q: I'm having problems with my Windows software. Will you help me?
- Q: Where can I find some real hackers to talk with?
- Q: Can you recommend useful books about hacking-related subjects?
- Q: Do I need to be good at math to become a hacker?
- Q: What language should I learn first?
- Q: What kind of hardware do I need?
- Q: I want to contribute. Can you help me pick a problem to work on?
- Q: Do I need to hate and bash Microsoft?
- Q: But won't open-source software leave programmers unable to make a living?
- Q: Where can I get a free Unix?
| Q: | How do I tell if I am already a hacker? |
| A: | Ask yourself the following three questions:
The first test is about skills. You probably pass it if you have the minimum technical skills described earlier in this document. You blow right through it if you have had a substantial amount of code accepted by an open-source development project. The second test is about attitude. If the five principles of the hacker mindset seemed obvious to you, more like a description of the way you already live than anything novel, you are already halfway to passing it. That's the inward half; the other, outward half is the degree to which you identify with the hacker community's long-term projects. Here is an incomplete but indicative list of some of those projects: Does it matter to you that Linux improve and spread? Are you passionate about software freedom? Hostile to monopolies? Do you act on the belief that computers can be instruments of empowerment that make the world a richer and more humane place? But a note of caution is in order here. The hacker community has some specific, primarily defensive political interests — two of them are defending free-speech rights and fending off "intellectual-property" power grabs that would make open source illegal. Some of those long-term projects are civil-liberties organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation, and the outward attitude properly includes support of them. But beyond that, most hackers view attempts to systematize the hacker attitude into an explicit political program with suspicion; we've learned, the hard way, that these attempts are divisive and distracting. If someone tries to recruit you to march on your capitol in the name of the hacker attitude, they've missed the point. The right response is probably “Shut up and show them the code.” The third test has a tricky element of recursiveness about it. I observed in the section called “What Is a Hacker?” that being a hacker is partly a matter of belonging to a particular subculture or social network with a shared history, an inside and an outside. In the far past, hackers were a much less cohesive and self-aware group than they are today. But the importance of the social-network aspect has increased over the last thirty years as the Internet has made connections with the core of the hacker subculture easier to develop and maintain. One easy behavioral index of the change is that, in this century, we have our own T-shirts. Sociologists, who study networks like those of the hacker culture under the general rubric of "invisible colleges", have noted that one characteristic of such networks is that they have gatekeepers — core members with the social authority to endorse new members into the network. Because the "invisible college" that is hacker culture is a loose and informal one, the role of gatekeeper is informal too. But one thing that all hackers understand in their bones is that not every hacker is a gatekeeper. Gatekeepers have to have a certain degree of seniority and accomplishment before they can bestow the title. How much is hard to quantify, but every hacker knows it when they see it. |
| Q: | Will you teach me how to hack? |
| A: | Since first publishing this page, I've gotten several requests a week (often several a day) from people to "teach me all about hacking". Unfortunately, I don't have the time or energy to do this; my own hacking projects, and working as an open-source advocate, take up 110% of my time. Even if I did, hacking is an attitude and skill you basically have to teach yourself. You'll find that while real hackers want to help you, they won't respect you if you beg to be spoon-fed everything they know. Learn a few things first. Show that you're trying, that you're capable of learning on your own. Then go to the hackers you meet with specific questions. If you do email a hacker asking for advice, here are two things to know up front. First, we've found that people who are lazy or careless in their writing are usually too lazy and careless in their thinking to make good hackers — so take care to spell correctly, and use good grammar and punctuation, otherwise you'll probably be ignored. Secondly, don't dare ask for a reply to an ISP account that's different from the account you're sending from; we find people who do that are usually thieves using stolen accounts, and we have no interest in rewarding or assisting thievery. |
| Q: | How can I get started, then? |
| A: | The best way for you to get started would probably be to go to a LUG (Linux user group) meeting. You can find such groups on the LDP General Linux Information Page; there is probably one near you, possibly associated with a college or university. LUG members will probably give you a Linux if you ask, and will certainly help you install one and get started. |
| Q: | When do you have to start? Is it too late for me to learn? |
| A: | Any age at which you are motivated to start is a good age. Most people seem to get interested between ages 15 and 20, but I know of exceptions in both directions. |
| Q: | How long will it take me to learn to hack? |
| A: | That depends on how talented you are and how hard you work at it. Most people who try can acquire a respectable skill set in eighteen months to two years, if they concentrate. Don't think it ends there, though; in hacking (as in many other fields) it takes about ten years to achieve mastery. And if you are a real hacker, you will spend the rest of your life learning and perfecting your craft. |
| Q: | Is Visual Basic a good language to start with? |
| A: | If you're asking this question, it almost certainly means you're thinking about trying to hack under Microsoft Windows. This is a bad idea in itself. When I compared trying to learn to hack under Windows to trying to learn to dance while wearing a body cast, I wasn't kidding. Don't go there. It's ugly, and it never stops being ugly. There is a specific problem with Visual Basic; mainly that it's not portable. Though there is a prototype open-source implementations of Visual Basic, the applicable ECMA standards don't cover more than a small set of its programming interfaces. On Windows most of its library support is proprietary to a single vendor (Microsoft); if you aren't extremely careful about which features you use — more careful than any newbie is really capable of being — you'll end up locked into only those platforms Microsoft chooses to support. If you're starting on a Unix, much better languages with better libraries are available. Python, for example. Also, like other Basics, Visual Basic is a poorly-designed language that will teach you bad programming habits. No, don't ask me to describe them in detail; that explanation would fill a book. Learn a well-designed language instead. One of those bad habits is becoming dependent on a single vendor's libraries, widgets, and development tools. In general, any language that isn't fully supported under at least Linux or one of the BSDs, and/or at least three different vendors' operating systems, is a poor one to learn to hack in. |
| Q: | Would you help me to crack a system, or teach me how to crack? |
| A: | No. Anyone who can still ask such a question after reading this FAQ is too stupid to be educable even if I had the time for tutoring. Any emailed requests of this kind that I get will be ignored or answered with extreme rudeness. |
| Q: | How can I get the password for someone else's account? |
| A: | This is cracking. Go away, idiot. |
| Q: | How can I break into/read/monitor someone else's email? |
| A: | This is cracking. Get lost, moron. |
| Q: | How can I steal channel op privileges on IRC? |
| A: | This is cracking. Begone, cretin. |
| Q: | I've been cracked. Will you help me fend off further attacks? |
| A: | No. Every time I've been asked this question so far, it's been from some poor sap running Microsoft Windows. It is not possible to effectively secure Windows systems against crack attacks; the code and architecture simply have too many flaws, which makes securing Windows like trying to bail out a boat with a sieve. The only reliable prevention starts with switching to Linux or some other operating system that is designed to at least be capable of security. |
| Q: | I'm having problems with my Windows software. Will you help me? |
| A: | Yes. Go to a DOS prompt and type "format c:". Any problems you are experiencing will cease within a few minutes. |
| Q: | Where can I find some real hackers to talk with? |
| A: | The best way is to find a Unix or Linux user's group local to you and go to their meetings (you can find links to several lists of user groups on the LDP site at ibiblio). (I used to say here that you wouldn't find any real hackers on IRC, but I'm given to understand this is changing. Apparently some real hacker communities, attached to things like GIMP and Perl, have IRC channels now.) |
| Q: | Can you recommend useful books about hacking-related subjects? |
| A: | I maintain a Linux Reading List HOWTO that you may find helpful. The Loginataka may also be interesting. For an introduction to Python, see the tutorial on the Python site. |
| Q: | Do I need to be good at math to become a hacker? |
| A: | No. Hacking uses very little formal mathematics or arithmetic. In particular, you won't usually need trigonometry, calculus or analysis (there are exceptions to this in a handful of specific application areas like 3-D computer graphics). Knowing some formal logic and Boolean algebra is good. Some grounding in finite mathematics (including finite-set theory, combinatorics, and graph theory) can be helpful. Much more importantly: you need to be able to think logically and follow chains of exact reasoning, the way mathematicians do. While the content of most mathematics won't help you, you will need the discipline and intelligence to handle mathematics. If you lack the intelligence, there is little hope for you as a hacker; if you lack the discipline, you'd better grow it. I think a good way to find out if you have what it takes is to pick up a copy of Raymond Smullyan's book What Is The Name Of This Book?. Smullyan's playful logical conundrums are very much in the hacker spirit. Being able to solve them is a good sign; enjoying solving them is an even better one. |
| Q: | What language should I learn first? |
| A: | XHTML (the latest dialect of HTML) if you don't already know it. There are a lot of glossy, hype-intensive bad HTML books out there, and distressingly few good ones. The one I like best is HTML: The Definitive Guide. But HTML is not a full programming language. When you're ready to start programming, I would recommend starting with Python. You will hear a lot of people recommending Perl, and Perl is still more popular than Python, but it's harder to learn and (in my opinion) less well designed. C is really important, but it's also much more difficult than either Python or Perl. Don't try to learn it first. Windows users, do not settle for Visual Basic. It will teach you bad habits, and it's not portable off Windows. Avoid. |
| Q: | What kind of hardware do I need? |
| A: | It used to be that personal computers were rather underpowered and memory-poor, enough so that they placed artificial limits on a hacker's learning process. This stopped being true in the mid-1990s; any machine from an Intel 486DX50 up is more than powerful enough for development work, X, and Internet communications, and the smallest disks you can buy today are plenty big enough. The important thing in choosing a machine on which to learn is whether its hardware is Linux-compatible (or BSD-compatible, should you choose to go that route). Again, this will be true for almost all modern machines. The only really sticky areas are modems and wireless cards; some machines have Windows-specific hardware that won't work with Linux. There's a FAQ on hardware compatibility; the latest version is here. |
| Q: | I want to contribute. Can you help me pick a problem to work on? |
| A: | No, because I don't know your talents or interests. You have to be self-motivated or you won't stick, which is why having other people choose your direction almost never works. Try this. Watch the project announcements scroll by on Freshmeat for a few days. When you see one that makes you think "Cool! I'd like to work on that!", join it. |
| Q: | Do I need to hate and bash Microsoft? |
| A: | No, you don't. Not that Microsoft isn't loathsome, but there was a hacker culture long before Microsoft and there will still be one long after Microsoft is history. Any energy you spend hating Microsoft would be better spent on loving your craft. Write good code — that will bash Microsoft quite sufficiently without polluting your karma. |
| Q: | But won't open-source software leave programmers unable to make a living? |
| A: | This seems unlikely — so far, the open-source software industry seems to be creating jobs rather than taking them away. If having a program written is a net economic gain over not having it written, a programmer will get paid whether or not the program is going to be open-source after it's done. And, no matter how much "free" software gets written, there always seems to be more demand for new and customized applications. I've written more about this at the Open Source pages. |
| Q: | Where can I get a free Unix? |
| A: | If you don't have a Unix installed on your machine yet, elsewhere on this page I include pointers to where to get the most commonly used free Unix. To be a hacker you need motivation and initiative and the ability to educate yourself. Start now... |

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)